
[기수정렬 이란]
여러 개의 큐를 이용해서 배열을 정리하는 방법
[알고리즘]
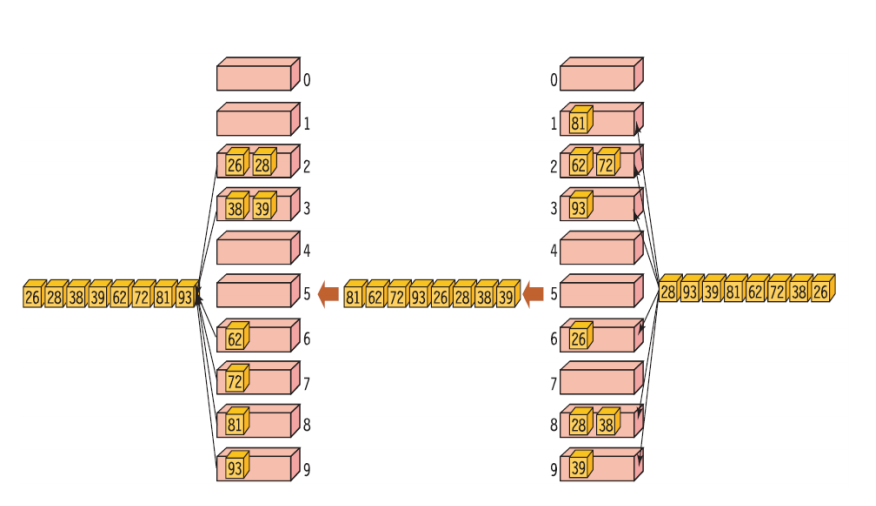
위 그림처럼 랜덤한 숫자를 오름차순으로 만드는 알고리즘 입니다.
첫번째로는 일의자리를 정렬하고
두번째로는 십의자리를 정렬합니다.
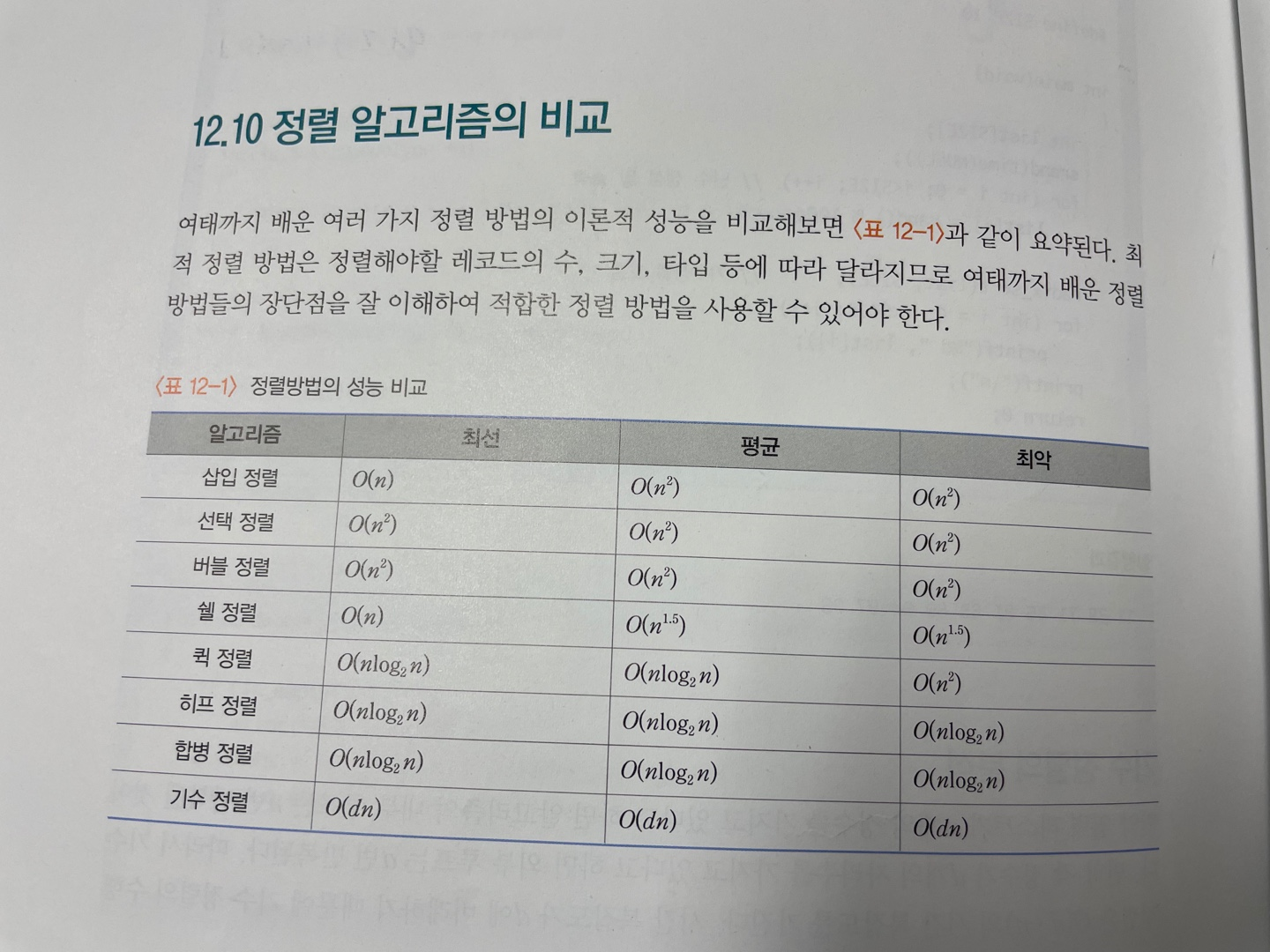
[시간 복잡도]
List[n]이 있으면 n번은 탐색을 합니다.
n 안의 숫자가 3자리라고 해도 1의 자릿수를 찾는 탐색을 n번
, 10의 자릿수를 찾는 탐색을 n번
, 100의 자릿수를 찾는 탐색을 n번 하기 때문에
d*n 빅오표기법은 O(n)이 된다. 최악과 최선의 경우는 둘다 없습니다.
[코드]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 100
typedef int element;
typedef struct { //큐 타입
element data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int front, rear;
} QueueType;
//오류 함수
void error(const char *message)
{
fprintf(stderr, message);
exit(1);
}
//초기화 함수
void init_queue(QueueType* q)
{
q->front = q->rear = 0;
}
// 공백 상태 검출 함수
int is_empty(QueueType* q)
{
return (q->front == q->rear);
}
//포화 상태 검출 함수
int is_full(QueueType* q)
{
return ((q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE == q->front);
}
//삽입 함수
void enqueue(QueueType* q, element item)
{
if (is_full(q))
error("큐가 포화상태입니다");
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
q->data[q->rear] = item;
}
// 삭제 함수
element dequeue(QueueType* q)
{
if (is_empty(q))
error("큐가 공백상태입니다");
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
return q->data[q->front];
}
#define BUCKETS 10
#define DIGIST 4
void radix_sort(int list[], int n)
{
int i, b, d, factor = 1;
QueueType queues[BUCKETS];
for (b = 0; b < BUCKETS; b++) init_queue(&queues[b]); //큐들의 초기화
for (d = 0; d < DIGIST; d++) {
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) //데이터들을 자리수에 따라 큐에 삽입
enqueue(&queues[(list[i] / factor) % 10], list[i]);
for (i = b = 0; b < BUCKETS; b++) //버킷에서 꺼내어 list로 합친다.
while (!is_empty(&queues[b]))
list[i++] = dequeue(&queues[b]);
factor *= 10; //그 다음 자리수로 간다.
}
}
#define SIZE 10
int main(void)
{
int list[SIZE];
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) //난수 생성 및 출력
list[i] = rand() % 100;
radix_sort(list, SIZE); // 기수정렬 호출
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
printf("%d\n", list[i]);
return 0;
}<<코드 설명>>
구조체 QueueType을 선언해 줍니다.
MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 크기를 가지는 배열 선언
front와 rear을 0으로 초기화하여 원형 큐 선언
front와 rear가 같다면 공백
rear에 1을 더하고 MAX_QUEUE_SIZE로 나눈 나머지가 front와 같다면 포화
front는 0, rear가 99, MAX_QUEUE_SIZE가 100이라 하면
(99+1) % 100 = 0
이 성립하면 포화 상태
enqueue(&queues[(list[i] / factor) % 10], list[i]);
예를들어 list[1]=11이라 가정 했을때
11/1%10=1
enqueue(queues[1],11)
원형 큐 enqueue[1] 즉 1의자리 큐에 11을 삽입하는데front와 rear가 0이니
rear에 1을 더하고 % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE를 나누어 원형 큐가 원점으로 돌아오게 합니다물론 MAX_QUEUE_SIZE만큼 쌓이지 않으면 나머지는 0 이겠죠
q->data[q->rear] = item;
queuse[0]~queuse[9]
=> 큐 10개 선언
data[100] front, rear
=> 원형 큐 선언